Patents
1. EP20 203952 “Piezoelectric device comprising flexible single crystalline piezoelectric LiNbO3 and/or LiTaO3 films integrated on flexible substrate and methods for producing the same” A. Bartasyte, S. Margueron, G. Clementi, M. Ouhabaz, F. Bassignot (2020)
2. EP20 305575 “Layered solid element comprising a ferroelectric layer and method for manufacturing the same” A. Bartasyte, V. Astié, S. Kuprenaite (2020)
3. F19 02226 “Procédé de réalisation d’un système micro-électro-mécanique réalisé à partir d’une couche piézoélectrique ou ferroélectrique reportée”, A. Reinhardt, M. Bousquet, A. Bartasyte (2019)
4. F17 62805 “Procédé de fabrication de composite à couche mince ultra-plane” F. Bassignot, L. Gauthier-Manuel, A. Bartasyte (2017)
5. EP 3188367 “Perfectionnement aux transducteurs à ondes de volume guidées en surface” S. Ballandras, R. Salut, A. Bartasyte (2016)
6. EP2826078 “Dispositif à ondes acoustiques comprenant un cristal de niobate de lithium ou de tantalate de lithium de composition optimisée à faible coefficient TCF et procédé de fabrication dudit cristal” A. Bartasyte and O. Elmazria, Université de Lorraine (2012)
7. WO/2011/158022 “Sensing physical parameters using birefringence” A.M. Glazer, P.A. Thomas, N. Zhang, A. Bartasyte, D.S. Keeble, Oxford University and Warwick University (2011)
WO/2011/158022 « Sensing physical parameters using birefringence »
 Link to patent
Link to patentA.M. Glazer, P.A. Thomas, N. Zhang, A. Bartasyte, D.S. Keeble
Oxford University & Warwick University (2011)
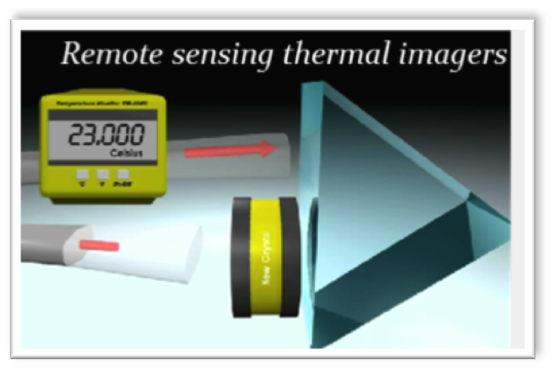
Description: Li0,988Ta1,012O3+d zero-birefringent single crystals was successfully obtained by vapour transport equilibration from commercial congruent LiTaO3 crystals. This allowed to fabricate remote thermal sensing imagers based on zero-birefringent crystals. These imagers present several advantages:
- No need for wire connections;
- Only the crystal in the environment;
- Remote light source, measurement & processing electronics;
- Independent on crystal thickness & orientation;
- Detection of temperature changes within mK range.
WO/2013/EP55454 ACOUSTIC WAVE DEVICE COMPRISING A LITHIUM NIOBATE AND/OR LITHIUM TANTALATE MATERIAL WITH AN OPTIMISED, LOW-TCF COMPOSITION, AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING SAID MATERIAL
 Link to patent
Link to patentA. Bartasyte and O. Elmazria
University of Lorraine (2012)
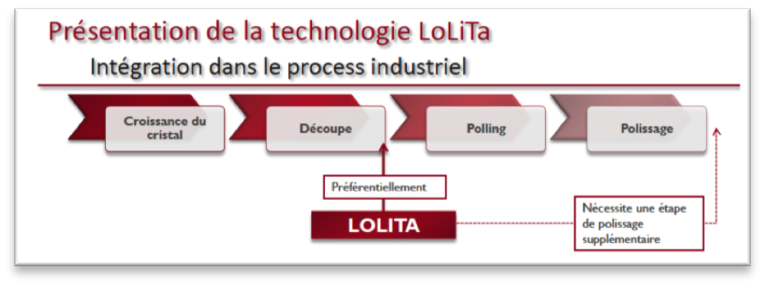
Description: Temperature coefficient of frequency of LiTaO3 single crystals was tuned by changing the Li stoichiometry. For this purpose, congruent 36° rotated Y-X crystals, available commercially, were treated by vapour transport equilibration (VTE). The TCF of leaky wave, propagating along X-axis, in 36° rotated Y-X LiTaO3 single crystals, used in SAW industry, was strongly improved in VTE treated wafers. TCF value was moved from -37.2 ppm/°C in congruent LiTaO3 crystal to -7 ppm/°C in LiTaO3 crystals with 49.43 mol% of Li2O, obtained by vapor transport equilibration. Moreover, the VTE process can be applied on big wafers and integrated to the industrial manufacturing of wafers without significant increase of costs (schematic representation of VTE process integration to the wafers manufacturing line is given above).
FR20150063360 IMPROVEMENT TO SURFACE-GUIDED VOLUME WAVE TRANSDUCERS
 Link to patent
Link to patentS. Ballandras, A. Bartasyte, and R. Salut
frecInIsys and CNRS (2015)
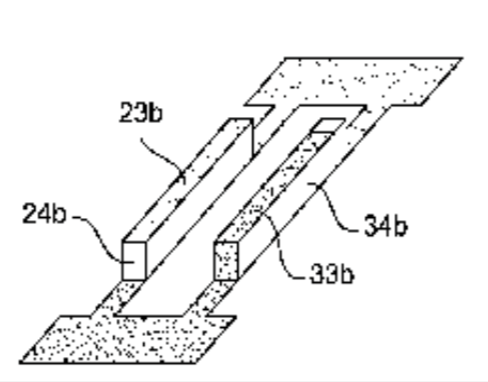
Description: L'invention concerne un transducteur à ondes de volume guidées, comprenant une plaque de substrat acoustique en matériau électriquement isolant et un réseau de sources d'excitation acoustique synchrones, le réseau comportant un premier peigne et un deuxième peignecomprenant chacun une pluralité de transducteurs élémentaires, les transducteurs élémentaires du premier et du deuxième peigne étant inter-digités et rangés selon une direction (X) de propagation des ondes de volume guidées, les transducteurs élémentaires s'étendant chacun selon un axe transversal (Y). Un transducteur selon l'invention est caractérisé en ce que chaque transducteur élémentaire comprend une électrode inférieure conductrice positionnée sur le substrat, un barreau en matériau piézoélectrique positionné sur l'électrode inférieure et une électrode supérieure conductrice positionnée sur le barreau. Application par exemple à la réalisation de transducteurs acoustiques embarqués sans fil et sans source d'énergie embarquée.

